
PROJECT MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES (AI) 5ed (New Edition)
Author: Rory Burke
Professor of Project Management 4.0
ISBN: print: 978-0-9941492-9-9
ebook: 978-1-99-117370-6
Published: 2023
Pages: 448
Price: £29.95, US$34.95, EUR35, AUD$59.95, R575

Project Management Techniques (AI) 5ed is fully updated to include the latest project management planning and control techniques to enable the project manager to achieve project success. This includes the Principles as outlined in the new PMBOK, expanded Sustainable project management, expanded Agile project management and a new chapter on how AI techniques can be used to plan and control projects.
The chapters are presented in a logical sequence which forms the structure of project management courses. The content of the chapters clearly explains the structure of all the subject areas, with plenty of definitions, worked examples and exercises.
The text book is supported with additional Power Point slides and MCQs for lecturers prescribing the text.
This book is designed to support:
Project Management Techniques (AI) 5ed includes the following chapters:
Ch 1: Introduction to PMT (AI) 5ed: The first chapter introduces the basic definitions that underpin project management and introduces the topics discussed in this book. This includes; what is a project, types of projects, what is project management, Sustainable project management (expanded), Role of the project manager, project-based Principles (PMBOK 7) and Agile project management (expanded).
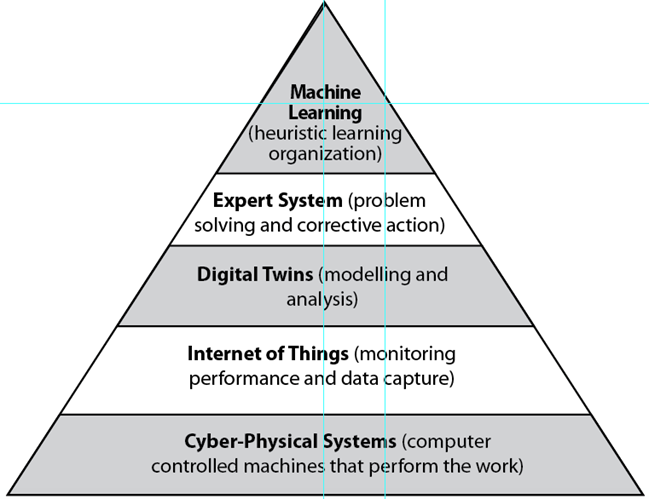
Ch 2: PM–AI (New Chapter) : This chapter shows how AI techniques can be used to plan and control projects. The chapter is structured around the Hierarchy of Artificial Intelligence from cyber-physical systems (industrial robots, drones and 3D printing), Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, Digital Twin modeling, Augmented Reality (AR) and Expert Systems (problem solving), to Machine Learning (learning organization).
As we enter the early stages of the Industry 4.0 economy, AI planning and control techniques are going to become more powerful and beneficial.
Ch 3: Project Lifecycle: This chapter shows how the Project or Product Lifecycle can be subdivided into a number of Phases, where each Phase produces a distinct deliverable or result. As a project progresses it passes through a number of these phases from conception to completion. Topics include; Lifecycle Costing and Lifecycle Contracts.
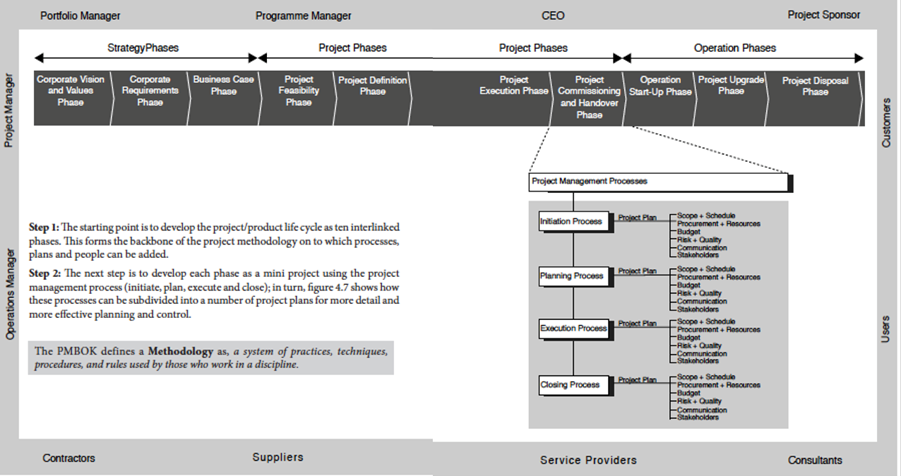
Ch 4: Portfolio and Programme Management: This chapter explains the difference between Portfolio Management, Programme Management and Project Management. Topics include, the extent of responsibility, the project management process and the programme management’s systems approach where each component is interlinked like a thread.
Ch 5: Project Stakeholder Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to identify stakeholders and interested parties. Topics include the networking Internet of Things, the processes and activities that enable the project manager to ensure that the needs and expectations of the project stakeholders and interested parties are being addressed, and that the stakeholders are appropriately involved in the problem solving and decision-making process.
Ch 6: Business Case Strategy Phase: This chapter explains the special techniques used to determine the direction the company wants to take and how it intends to do business. Topics include; corporate vision, corporate requirements and how to write a business case.
Ch 7: Project Feasibility Phase: This chapter explains the special techniques used to determine if the project is capable of achieving the business case objectives. Topics include; how to write a Project Charter, how to identify the Client’s Requirements, the Internal Project Constraints and External Constraints.
Ch 8: Project Definition Phase: This chapter explains the special techniques used to develop the business case into detailed project design and a fully integrated Project Plan. Topics include; the Project Design Process, Model Testing and Operational Configuration.
Ch 9: Project Execution Phase: This chapter explains the special techniques used to manufacture or implement the project deliverables. Topics include; the Project Build-Method and the Project Execution Strategy.
Ch 10: Project Commissioning and Handover Phase: This chapter explains the special techniques used to commission the project to officially verify, test and document that the project has been completed to the required condition. Topics include; the Handover Process, how to Terminate the project and the Project Closeout Report.
Ch 11: Operational Phases: This chapter explains the special techniques used to manage embedded projects within the operational phases. Topics include; the Operational Start-up phase, the Project Upgrade phase and the Project Disposal phase.
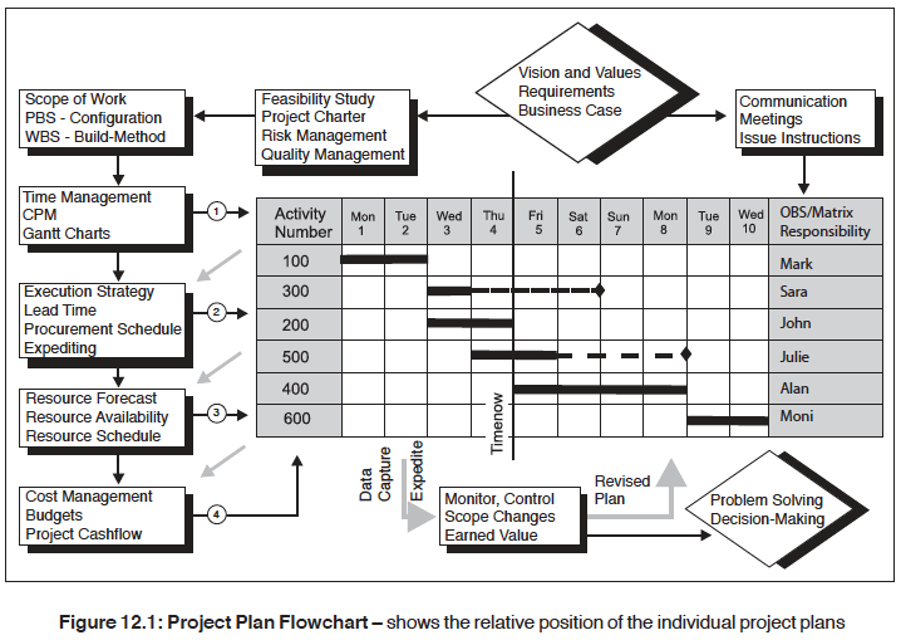
Ch 12: Project Plan: This chapter explains the special techniques used to integrate all the individual plans to produce the Project Plan. Topics include; the Project Plan Flowchart, the Project Plan Spiral. A key feature of the Project Plan is the Agile approach to managing the trade-offs and compromises between the individual plans so that the Project Plan can converge on an optimum arrangement.
Ch 13: Project Scope Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to identify all the work required to achieve the project objectives. Topics include; Scope Definition, Scope Change Control, Scope Validation and Verification.
Ch 14: WBS: This chapter explains the special techniques used to subdivide the scope of work into manageable Work Packages. Topics includes; the WBS, the Product Breakdown Structure, Methods of Subdivision, Numbering System and WBS Templates.
Ch 15: Project Schedule Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to plan and control the project’s schedule. Topics include; definition of an Activity, Project Calendar, and Estimating an Activity’s Duration.
Ch 16: CPM: This chapter explains the special techniques used to enable the project manager determine all the activities start and finish dates. Topics include; the Network Diagram and the Critical Path Method (identify critical path).
Ch 17: Gantt Charts: This chapter explains the special techniques used to present schedule information. Topics include; the Gantt Chart, the Schedule Barchart, Hammock Activities and Milestone charts.
Ch 18: Project Procurement Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to processes and activities that enable the project manager to acquire the goods and services required to perform the project’s scope of work. Topics include; the Project Procurement Process, JIT, Procurement Schedule and Procurement Expediting.
Ch 19: Request for Proposal (RFP): This chapter explains the special techniques used to officially request information, products or services. Topics include; Request for Information (RFI), Request for Proposal (RFP) and Request for Quotation (RFQ).
Ch 20: Project Resource Scheduling: This chapter explains the special techniques used to link the project resource requirements with the company’s resource pool and the project plan. Topics include; the Resource Histogram, Resource Loading, Resource Smoothing, Time-Limited Resource Scheduling and Resource-Limited Resource Scheduling.
Ch 21: Project Cost Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to enable the project manager to complete the project within budget. Topics include; the Estimating Continuum, Top-Down and Bottom-Up Estimating, Estimating Costs, Labour Costs, Procurement Costs, Unit Rates and Establishing Budgets.
Ch 22: Project Cash Flow: This chapter explains the special techniques used to project manage the flow of monies through the project’s account. Topics include; the Cash-Flow Statement, Cash-Flow Timing, Invoicing, Cost-to-Complete and how to draw the Expense ‘S’ Curve.
Ch 23: Project Control: This chapter explains the special techniques within the project integration knowledge area that enables the project manager to monitor and control the project’s progress. Topics include; Monitoring Progress, Problem Solving and Decision-Making.
Ch 24: Earned Value: This chapter explains the special techniques within the project integration knowledge area that enables the project manager to plan and control the project’s progress in comparable units. Topics include; How to Draw the Earned Value Curve (PV, EV and AV) and the Earned Value Table.
Ch 25: Quality Management: This chapter explains the special techniques and processes used to ensure that the project achieves the required condition. Topics include; Quality Planning, Quality Assurance Plan, Quality Control Plan, Continuous Improvements and Quality Circles.
Ch 26: Risk Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to identify and manage the risks that would prevent the project achieving its objectives. Topics include; the Risk Management Process, Risk Identification, Why Projects Fail, Risk Quantification and Risk Response.
Ch 27: Communication Management: This chapter explains the special techniques used to manage project data and information (generation, collection, distribution, storage, retrieval and ultimate disposal). Topics include; Communication Plan, Project Meetings, Project Reporting and Document Control.
Ch 28: Project Leadership and Entrepreneurship: This chapter explains the special techniques the project manager can use to lead and manage the project team and other project participants. Topics include; Leadership Traits, Leadership Power, Project Entrepreneurship, Management vs Leadership vs Entrepreneurship, Maslow, Herzberg, Conflict Management and Delegation.
Ch 29: Project Teams: This chapter explains the special techniques used to project manage multi-disciplined teams with the project office. Topics include; the Team Charter, Team Development Phases and Team Building Techniques.
Ch 30: Project Organization Structures: This chapter explains the special techniques within the human resource knowledge area that enables the project manager to lead and manage a multidiscipline project organization. Topics include; Functional Organization Structures, Matrix Organization Structures and Pure Project Organization Structures.
Append 1: Project Selection: The selection of the right project for future investment is a crucial decision for the long term survival of the company. Worked examples include; Payback Period, Return on Investment, Discounted Cash Flow, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return and Breakeven Analysis.
Append 2: Project Management in the Fourth Industrial Revolution – Prof. Pieter Steyn: Explains how project management techniques, the Industry 4.0 economy, are assuming a much more important holistic role and influence in the governance of organisational value chains than ever before.